How Many Molecules Are There in a Grin of Silica Sand? To answer the question, how many molecules are there in a grain of silica sand?, you can use the same principle as when calculating the number of molecules in a piece of paper. A grain of sand has a volume of 0.001 cm3 and a relative molecular mass of 64. This means that there are two times as many atoms in a grain of sand as there are in all of the world’s population.
A grain of sand is the smallest thing on earth and contains less than 0.03% water. So a rough estimate of sand’s density would be too difficult. But, if we want to get an accurate answer to the question, we should remember that atoms are separated by a few Angstroms. In fact, 50 million of them are scattered around a centimetre.
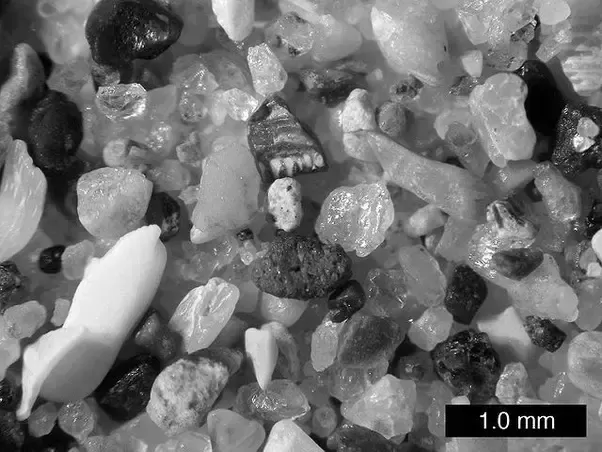
A grain of sand is composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), a mineral with the formula SiO2. Silica consists of two chemical elements: silicon and oxygen. Both elements weigh approximately 28 atomic units. Combined, they total 60 atomic units. This means that one gram of sand contains more than 6.023 x 1023 atoms.
Earth’s beaches are estimated to contain 7.5 x 1018 grains of sand. This means that there are roughly five hundred quadrillion grains of sand on Earth. In fact, half of those grains are atoms. That makes the grains of sand nearly half as dense as a human hair. So, the answer is 163 billion grains per square metre of beach.

How many atoms are in a molecule?
How do you calculate number of molecules?
How do you calculate molecules?
In order to calculate the number of molecules in a sample, you need to know the molar mass of the substance. The molar mass is the mass of one mole of the substance, and it is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule. Once you have the molar mass, you can use the following formula:
Number of molecules = Mass of sample / Molar mass of substance
For example, let’s say you have a sample of water that has a mass of 10 grams. The molar mass of water is 18.015 g/mol, so the number of molecules in the sample can be calculated as follows:
Number of molecules = 10 g / 18.015 g/mol = 0.555 mol
This means that there are approximately 555 million water molecules in the 10 gram sample.
What are 3 types of molecules?
Molecules are the basic units of matter and the defining structure of elements and compounds. The term “molecule” was first used in a scientific context by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. The atoms in a molecule are held together by chemical bonds. There are three types of molecules: covalent, polar covalent, and ionic.
Covalent molecules are held together by covalent bonds, which are formed when two atoms share electrons. In a covalent bond, each atom contributes one or more electrons to the bond. The electrons are shared equally between the atoms. Covalent molecules are typically non-polar.
Polar covalent molecules are held together by covalent bonds, but the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms. One atom has a greater electronegativity than the other, so it attracts the shared electrons more strongly. This creates a dipole, with the negative pole (the electron-rich atom) at one end and the positive pole (the electron-poor atom) at the other. Polar covalent molecules are typically polar.
Ionic molecules are held together by ionic bonds, which are formed when one atom donates electrons to another atom. In an ionic bond, one atom becomes positively charged (cation) and the other atom becomes negatively charged (anion). The atoms are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force. Ionic molecules are typically polar.
What is the size of 1 molecule?
What are 5 examples of molecules?
In chemistry, a molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. However, in quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the term molecule is often used less strictly, also being applied to polyatomic ions.
In the simplest view of a molecule as a perfect, rigid, spherical shell, the bond angles and the lengths of the bonds are fixed. In this so-called “static” view, the molecule does not vibrate, rotate, or translate as a whole. In reality, however, molecules are never completely still because they are always undergoing thermal motion, even at very low temperatures (absolute zero is unattainable). Atoms and molecules are always in motion, and this motion is characterized by a distribution of kinetic energies.
The term molecule is derived from the Latin word moles or molecula, meaning “little mass” or “little particle”. The word molecula originally referred to very small particles of matter, but in modern usage it generally refers to microscopic particles of solid, liquid, or gas. The word molecule is also used in other contexts in chemistry and physics, such as in the terms molecular weight, molecular structure, and molecular orbital.
A molecule consists of a group of atoms held together by chemical bonds. The atoms in a molecule can be held together by a variety of different types of bonds, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds. In a covalent bond, the atoms share electrons, and the bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nuclei and the shared electrons. In an ionic bond, the atoms are held together by the electrostatic attraction between opposite charges, and the bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to the other. In a hydrogen bond, the atoms are held together by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged hydrogen atom and a negatively charged atom, and the bond is formed by the sharing of the hydrogen atom’s electron.
The strength of the bonds between the atoms in a molecule determines the molecule’s stability and its properties. The types of bonds present in a molecule also determine the molecule’s reactivity. For example, molecules with multiple bonds are generally more stable than molecules with single bonds, and molecules with ionic bonds are generally more reactive than molecules with covalent bonds.
The size of a molecule is determined by the number of atoms it contains. The vast majority of molecules are very small, containing only a few atoms. However, there are some molecules that are quite large, containing thousands of atoms. The largest known molecule is buckminsterfullerene, which contains 60 carbon atoms.
The shape of a molecule is determined by the arrangement of the atoms it contains. The simplest molecules, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are linear, meaning that the atoms are arranged in a straight line. More complex molecules can be linear or nonlinear. The shapes of molecules are important in determining their properties and their reactivity.
Molecules can be classified in a variety of ways, including by their size, shape, and the types of bonds they contain. The five examples of molecules below illustrate some of the diversity among molecules.
-
Methane (CH4)
Methane is a gas at room temperature and pressure, and it is the simplest molecule containing only carbon and hydrogen. The carbon atom in methane is bonded to four hydrogen atoms, and the molecule has a tetrahedral shape. Methane is the main component of natural gas, and it is used as a fuel for heating and cooking.
-
Water (H2O)
Water is a liquid at room temperature and pressure, and it is composed of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. The shape of the water molecule is bent, and the molecule is said to be polar because the oxygen atom has a greater electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms. Water is a major component of all living things, and it is essential for life.
-
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide is a gas at room temperature and pressure, and it is composed of one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms. The carbon dioxide molecule is linear, and the molecule is said to be polar because the oxygen atoms have a greater electronegativity than the carbon atom. Carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas, and it is responsible for the greenhouse effect.
-
Nitrogen (N2)
Nitrogen is a gas at room temperature and pressure, and it is composed of two nitrogen atoms bonded to each other. The nitrogen molecule is linear, and the molecule is said to be nonpolar because the nitrogen atoms have the same electronegativity. Nitrogen is an important component of the atmosphere, and it is used in the manufacture of fertilizers.
-
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA is a molecule composed of two strands of nucleotides, and it is the molecule that encodes the genetic information of all living things. DNA is double-stranded, and the strands are held together by hydrogen bonds. The DNA molecule is said to be helical, and the molecule is very large, containing millions of atoms.
Is water a molecule?
Can humans make water?
Can humans make water? The short answer is no. Water is a naturally occurring substance that is essential for all life on Earth. While humans can’t create water, we can desalinate it or purify it for drinking.
Water is made up of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen (H2O). This combination of atoms is called a molecule. Water molecules are created when hydrogen and oxygen atoms bond together. The process of making water is called hydrogenation.
Humans can’t create hydrogen or oxygen atoms, so we can’t create water. However, we can desalinate water. Desalination is the process of removing salt and other minerals from water. This is usually done by distilling water or using a reverse osmosis filter.
While we can’t create water, we can conserve it. Water conservation is important because water is a limited resource. There are many ways to conserve water, such as using less water when you brush your teeth or water your plants.
So, while humans can’t create water, we can still play an important role in its cycle. By desalinating and conserving water, we can help ensure that there is enough water for everyone on Earth.
Is gold a molecule?
Conclusion
So how many molecules are there in a grain of sea sand? According to scientists, Earth has approximately 7.5 sextillion grains of sand. This means that each grain of sand contains more molecules than stars in the Universe. A grain of sea sand is approximately one-sixth the size of an atom. This is staggering. What’s more, a grain of sea sand contains more molecules than the planet Mercury.
Hello and goodbye! We hope you enjoyed our latest post How Many Molecules Are There in a Grin of Silica Sand? and found it informative.. We hope you had a great time browsing our website and found everything you were looking for. If not, please feel free to contact us and let us know how we can improve. We love hearing from our visitors and are always looking for ways to improve our website. So, thank you again for stopping by and we hope to see you soon!
Hey also do not forget to check out our: How Many Cups is 100 Oz of Water?
Today sponsor is Infinity Charm. Check out these amazing magnetic heart bracelets! They are great for anyone who wants to show their love, or simply wants to add a little bit of flair to their outfit. They are stylish and unique, and would make a great gift for someone special. Also check out this very beautiful Magnetic Couples Heart Necklaces and this very nice Virgencita Necklace.